KMU 396
MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY I
Instructor: Dr. Selis Önel
Midterm Examination, Thursday, April 2, 2009
You are allowed to use an A4 size information sheet, which you have to return with the exam paper. Please use English and give brief answers to the following questions:
Question 1.
Circle the correct word in the following sentence or fill in the blank:
a) A material in which atomic bonding is predominantly ionic in nature is less / more likely to form a noncrystalline solid upon solidification than a covalent material because covalent bonds are directional / nondirectional whereas ionic bonds are directional / nondirectional; it is less / more difficult for the atoms in a covalent material to assume positions giving rise to an ordered structure.
b) A crystal structure / system is described by both the geometry of, and atomic arrangements within, the unit cell, whereas a crystal structure / system is described only in terms of the unit cell geometry. For example, face-centered cubic and body-centered cubic are crystal structures / systems that belong to the cubic crystal system.
c) The vacancy concentration in a crystal structure increases with ______________.
d) The surface energy of a single crystal depends on crystallographic orientation / number of grain boundaries because the atomic packing is different for the various crystallographic planes, and, therefore, the number of unsatisfied bonds will vary from plane to plane.
(b) The surface energy will be greater / less for an FCC (100) plane than for a (111) plane because the (111) plane is more / less densely packed (i.e., has more / less nearest neighbor atoms in the plane); as a consequence, more / less atomic bonds will be satisfied for the (111) plane, giving rise to a lower surface energy.
Question 2.
Information in the table is adapted from Callister 6th ed., p.23
|
Substance |
Bonding Energy eV/Atom, Ion, Molecule |
Melting Temperature (oC) |
Bonding Type |
Material Type |
|
W |
8.8 |
3410 |
|
|
|
MgO |
5.2 |
2800 |
|
|
|
NH3 |
0.36 |
-78 |
|
|
|
C (diamond) |
7.4 |
>3550 |
|
|
|
Hg |
0.7 |
-39 |
|
|
|
Al |
3.4 |
660 |
|
|
|
H2O |
0.52 |
0 |
|
|
|
Si |
4.7 |
1410 |
|
|
|
Ar |
0.08 |
-189 |
|
|
|
Cl2 |
0.32 |
-101 |
|
|
|
NaCl |
3.3 |
801 |
|
|
|
Fe |
4.2 |
1538 |
|
|
a) Indicate the bonding type, ionic, covalent, metallic, van der Waals, or hydrogen, for each substance on the table
b) Which would you expect to have higher modulus of elasticity (E), Al or Si? Explain.
c) Indicate the ceramic and metallic materials on the table
d) Make a simple plot of the bonding energy versus melting temperature for the metals listed in the table. Using the plot calculate/estimate the bonding energy for Cu, which has a melting temperature of 1084 oC.
Question 3.
Determine the Miller indices for the lattice points, directions and planes in the following figures. Show beneath or next to each answer box how you obtained your results (as shown in the example)

![]()
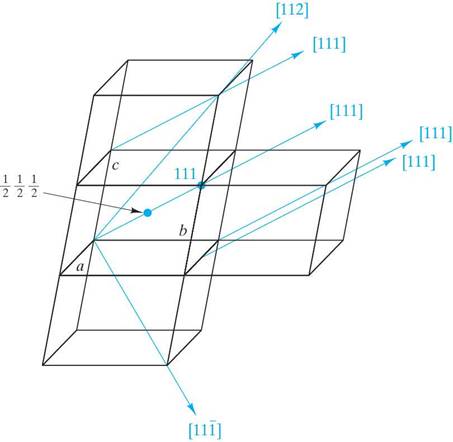
Example ( )
![]()
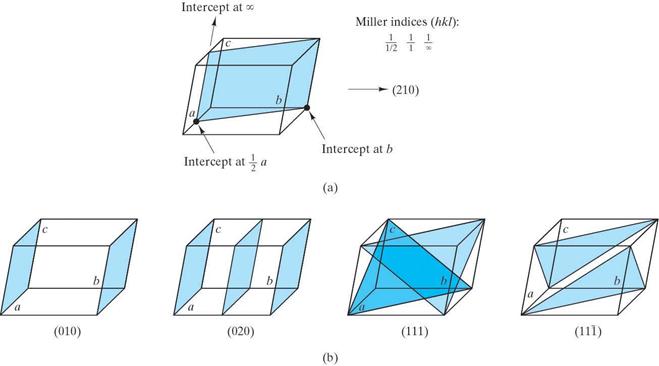
Question 4.
The following XRD pattern is obtained for a sample using monochromatic radiation with wavelength of 1.54089 Å.
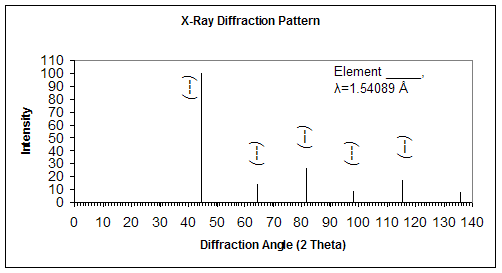
a) Determine the interplanar spacing for each of the peaks
b) Index each of the peaks (Determine the indices h, k, l)
c) Determine the crystal structure and select which of the following materials this sample could be: Cr, Cu, Zn
d) Determine the lattice parameter and the atomic radius
Question 5.
a) What is the typical dislocation density in the softest metals in cm/cm3 and what densities can be achieved by deforming these metals?
b) What would happen to the electrical conductivity of pure Cu with increasing dislocation density and why?
c) If no dislocations were present in a metal, would be ductile or brittle? Why?
d) What is meant by plastic and elastic deformation (also show graphically) and why is the theoretical strength of metals higher than that observed experimentally on the order of 103 to 104 ?