|
|
BUS 323
FINAL
EXAMINATION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SCHEDULE ASSIGNMENTS Assignment
1 RESULTS
|
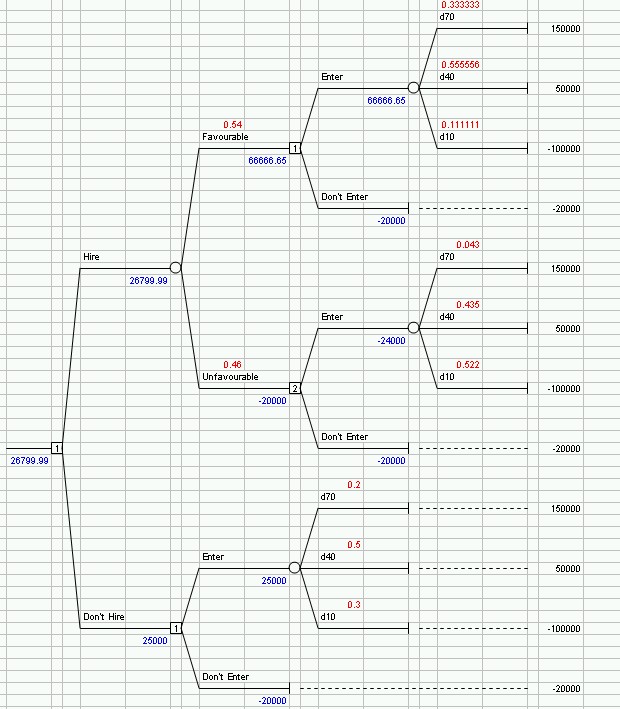
1) (50 points) Bees Candy Company must decide whether or not to introduce a new lower-calorie candy assortment for Christmas. Management feels that if it introduces the candy, it will earn a profit of $150,000 if sales are 70,000 pounds and a profit of $50,000 if sales are 40,000 pounds. It will lose $100,000 if sales are only 10,000 pounds. If Bees does not introduce the lower-calorie candy assortment, it believes it will lose $20,000 due to lost sales.
a. Construct a payoff table for this problem. Sales 70,000 40,000 10,000 Introduce 150 50 -100 Do Not Intro. -20 -20 -20
b. Should Bees introduce the candy if management is conservative?
A conservative strategy is the Maximin Criterion -- Do not introduce
c. Construct a regret table for this problem.
Sales 70,000 40,000 10,000 Introduce 0 0 $80 Do Not Introduce $170 70 0
d. If Bees management uses the minimax regret criterion, should the new candy be introduced?
Minimax Regret Criterion -- Introduce
Suppose Bees management believes that the following probabilities hold: P(Sales = 70,000 pounds) = .2 P(Sales = 40,000 pounds) = .5 P(Sales = 10,000 pounds) = .3 e. Using the expected value criterion, determine whether the company should introduce the lower-calorie candy assortment.
Sales 70,000 40,000 10,000 EV Introduce 150 50 -100 25 ß--- Do Not Intro. -20 -20 -20 -20 PROBABILITY 0.2 0.5 0.3
f. What is the most Bees management should pay for market research dealing with people’s attitudes toward the lower-calorie candy?
EV with PI = 150*0.2 + 50*0.5 + (-20)*0.3 = 49 EV of PI = EV with PI – EV = 49 – 25 = 24
Bees is considering hiring a market consulting firm to analyze people’s attitudes toward lower-calorie candy. The market research firm will report back to Bees management whether attitudes are favorable or unfavorable. Management believes that the following conditional probabilities hold: P(favorable attitudeuSales = 70,000 pounds) = .90 P(favorable attitudeuSales = 40,000 pounds) = .60 P(favorable attitudeuSales = 10,000 pounds) = .20 g. If the survey is performed and results in a favorable attitude toward lower-calorie candy, would you recommend that the candy be produced?
h. Determine the expected value of this sample information. 26800-25000=1800
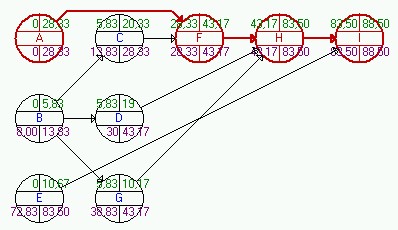
2) (25 points) George Washington High School is planning a reunion for the graduating class of 1975. The D’Onofrio twins, who are in charge of planning the entire event, have determined the following tasks.
What is the probability that the D’Onofrio twins will have to commit more than three months (90 days) to this project?
Critical Path: A-F-H-I Project Completion Time: 88.5 day Project St.Dev.: 6.56
z= (90-88.5)/6.56 = 0.23 For 0.23, the value from table is 0.091
P(Finish within 90 days) = 0.5 + 0.091 = 0.591 Thus P(Finish later than 90 days) = 1 - 0.591 = 0.409 = 40.9%
3) (25 points) BP Farms is a 300 acre farm located near Lawrence, Kansas, owned and operated exclusively by Bill Pashley. For the upcoming growing season, Bill will grow wheat, corn, oats, and soybeans. The following table gives relevant data
concerning expected crop yields, labor required, expected preharvested expenses, and water required. Also included is the price per bushel Bill expects to receive when the crops are harvested.
Bill wishes to produce at least 30.000 bushels of wheat and 30.000 bushels of corn but no more than 25.000 bushels of oats. He has $25.000 to invest in its crops, and he plans to work up tıo 12 hours per day during the 150-day season. He also does not wish to exceed the base water supply of 1200 acre-feet allocated to him by the Kansas Agriculture Authority.
a. Formulate the problem for BP farms as a linear program to maximize total expeceted return from the harvested crop.
X1 = the number of acres of wheat planted X2 = the number of acres of corn planted X3 = the number of acres of oats planted X4 = the number of acres of soybeans planted
Profit coefficients are 210($3.20) - $50 = $622, 300($2.55) - $75 = $690, 180($1.45) - $30 = $231, and 240($3.10) - $60 = $684 respectively.
MAX 622X1 + 690X2 + 231X3 + 684X4 S.T. 4X1 + 5X2 + 3X3 + 10X4 £ 1,800 (Labor hours) 50X1 + 75X2 + 30X3 + 60X4 £ 25,000 (Expenses) 2X1 + 6X2 + X3 + 4X4 £ 1,200 (Water) 210X1 ³ 30,000 (Min. Wheat) 300X2 ³ 30,000 (Min. Corn) 180X3 £ 25,000 (Max Oats) X1 + X2 + X3 + X4 £ 300 (Total acres) All X's ³ 0
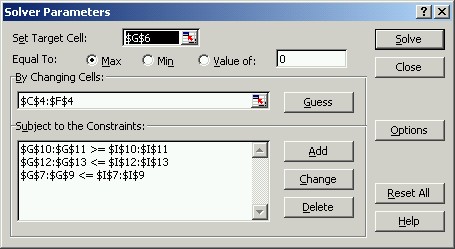
b. Create a spreadsheet model and define Solver parameters on the Excel and Solver figures below
c. Show the formulas in the cells, G6, G7, ...., G13.
G6: =SUMPRODUCT($C$4:$F$4;C6:F6) Copy to G6:G13
d. Interpret the numbers shown bold on the sensitivity report.
690: Objective coefficient of oats -444: For oats to have a positive value at the solution, objective coefficient of oats must be increased this amount. 28: Objective coefficient of soybeans can be decreased this amount wthout changing the solution. 371,429: Labor availability(1800) can be decreased this amount without being a binding constraint. 3: For every 1 additional unit of available water, objective value will increase this amount. -0.2667: For every 1 additional unit of necessary wheat production, objective value will decrease this amount.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||