|
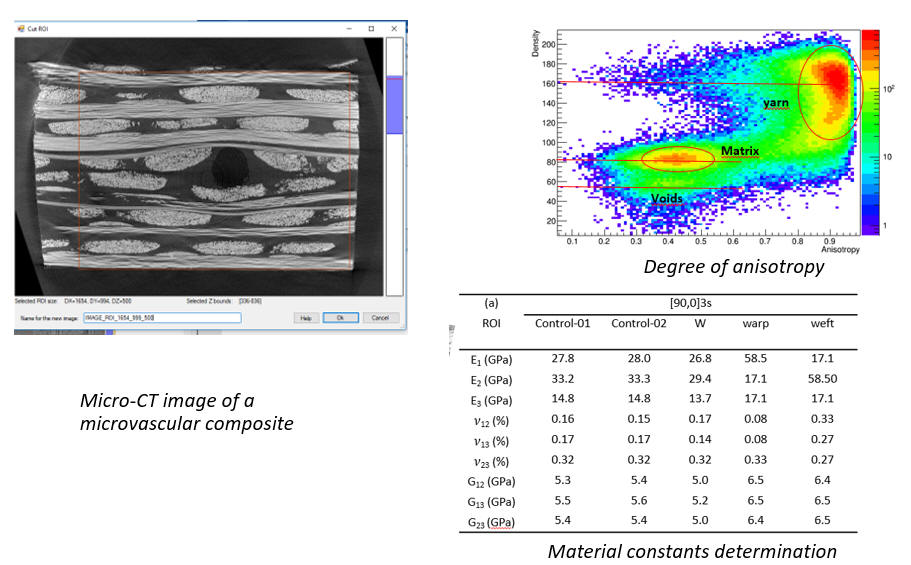
Sample Completed Projects Measurement of fiber orientation and composite properties via micro-CT imaging in composites with microvascular channels Collaborators: KU Leuven / Belgium , University of Turkish Aeronautical Assocation Abstract: Microvascular channels, embedded in fber-reinforced composites are introduced as an efcient tool for internal damage monitoring, self-healing, and thermal management applications. As an adverse effect, vascular channels cause a disturbance in the fbers around the channel region. In this study, frst, the fber orientation around the channel is evaluated using micro-CT images analyzed with VoxTex software. Variation in the stiffness around the channels is determined using micro-homogenization.
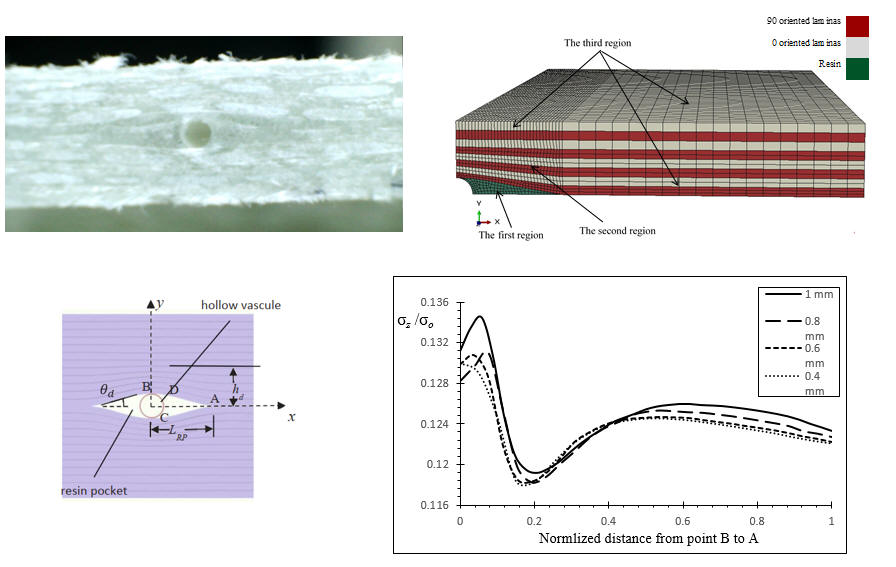
Investigation of stress distributions in the resin-rich region in composites with microvascular channels Collaborators: University of Turkish Aeronautical Assocation
Abstract:As an adverse effect
of microvascular channels, presence of such channels can harm the
mechanical behavior of composites. In the present study, 3D models are
generated to investigate the stress concentrations in the resinrich
pocket and failure behavior considering different
stacking configuration
and vascule sizes.
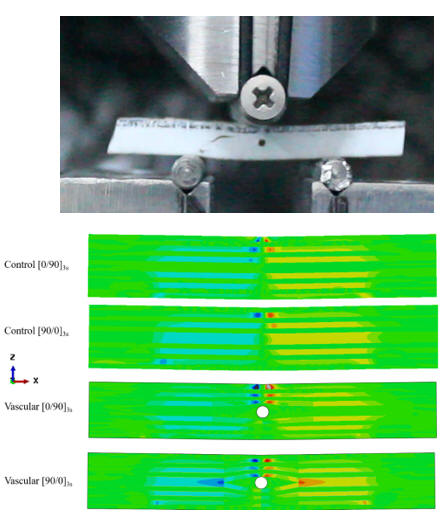
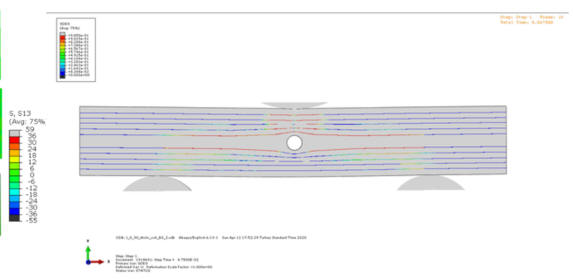
Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Transverse Shear Behaviour in Composites with Micro-vascular Channels Collaborators: American University of the Middle East, Kuwait
Abstract:Interply and interplay damage behavior of
glass fiber
composites with microvascular channels were investigated in this
study. Short beam flexural
tests and finite
element analysis were performed according to ASTM D2344 for two
stacking configurations,
[90/0]3s and [0/90]3s. Specimens with and without channel (control
specimens) were analyzed to investigate the channel effect in detail.
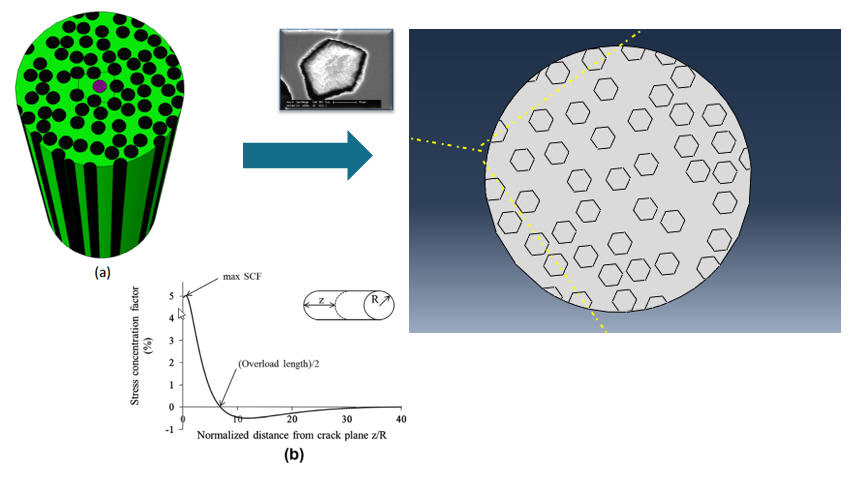
Stress Concentrations due to Fiber Break in Steel Fiber Composites Collaborators: KU Leuven / Belgium, Middle East Technical University
Abstract: A parametric study was performed to
investigate the stress concentrations due to a fiber break by
using 3D
finite element models with randomly
distributed and oriented hexagonal
fibers. The effect plastic behavior
was also included in this study
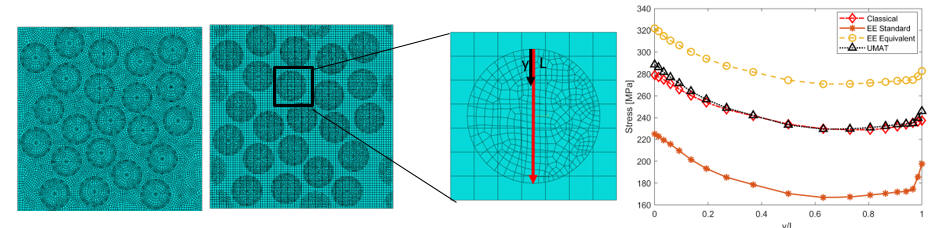
Development of embedded element modelling technique to include material nonlinearity Collaborators: Middle East Technical University
Abstract: Embedded element method is considered to be
a reliable and efficient
method to analyze the mechanical behavior of composite materials.
However, the predicted behavior of individual constituents can be
inaccurate in case the fiber
stiffness is close to the matrix stiffness and matrix nonlinearity is
present. The redundant volume existing in the embedded region causes
this problem. In this work, a procedure that solves this redundant
volume problem is developed while considering the matrix non‐linearity.
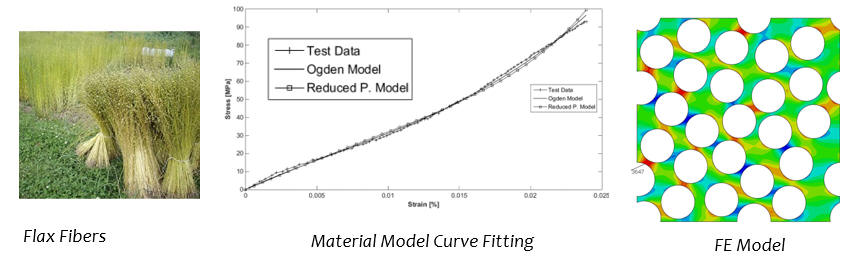
Fiber-matrix interface stresses in flax-fiber composites Collaborators: Middle East Technical University
Distribution of stresses in fiber/matrix
interface in UD flax fiber reinforced composites is investigated under
transverse
|